Availability Manager
This facility lets you manage the ActiveBatch Job Scheduler high availability (HA) features of the product. If your active Job Scheduler fails, one or more standby Job Schedulers can take over, avoiding loss of availability. The Availability Manager supports managing the ActiveBatch non-cluster failover HA solution offered by ASCI. The non-cluster failover is a separately licensed feature.
There is a GUI based Availability Manager and a command-line utility. The first option discussed is the GUI Availability Manager.
Availability Manager - GUI access
You can access the availability manager through ActiveBatch Console via Tools > Availability Manager.
Note: You must have proper read-write access to the Job Scheduler’s database to access the proper Availability table.
If you are currently connected to a Job Scheduler, ActiveBatch will attempt to use the database connection string that Job Scheduler uses. In this case, the Featuretest machine will be accessed and its Availability table displayed.
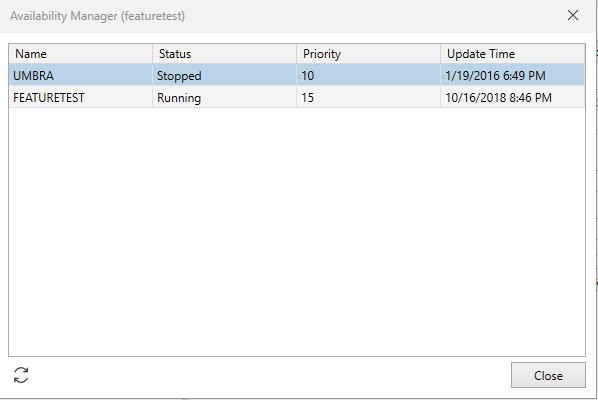
You may select any of the following operations:
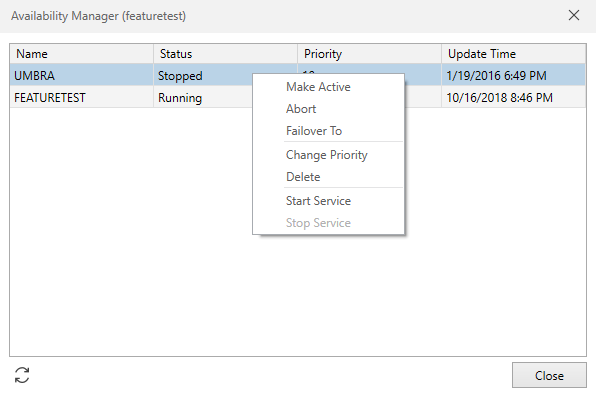
Make Active. This operation allows you to select a specific machine and make it the active Job Scheduling system. This action will implicitly stop any other active Job Scheduler machine so you should use this command when no other Job Scheduler machine is active and use the Failover to operation when you explicitly want to switch Job Scheduler machines.
Abort. This operation aborts the selected Job Scheduler service. Failover processing will occur automatically using ActiveBatch availability rules.
Failover to. This operation causes the selected machine to become the active Job Scheduling system. If an active machine is already present that machine will be aborted.
Change Priority. This operation allows you to modify the priority of the failover machine within its set. The priority allows you precise control as to the ordering of machines that should assume Job Scheduling. The higher the priority, the more preference for that machine assuming Job Scheduling responsibility.
Delete. This operation will delete the database entry for the selected machine. Note: The machine selected cannot be the active Job Scheduling system.
Start/Stop Service. These operations allow you to control whether the selected Job Scheduler service is to be started or stopped. Note: You can also use the ActiveBatch Service Manager utility (under the Tools menu) for more precise control.
Note: You must ‘Refresh’ the window whenever you make a modification to obtain the latest data. The Refresh button is present for that purpose.
Availability Manager – Command Line
Abatavlmgr is the ActiveBatch Availability Manager for non-cluster failover. AbatAvlMgr can be executed from a Powershell or CMD console (you must also have proper access to the underlying Job Scheduler’s database) and supports the following syntax:
Abatavlmgr command qualifiers
| Command | Description | Qualifiers |
|---|---|---|
| Abort | This command allows you to abort and stop a Job Scheduler machine service. |
-d connection-string -m machine-name -u username -p password |
| Active | This command allows you to designate an active Job Scheduler machine. This command is obeyed only when a Job Scheduler machine isn’t already active |
-d connection-string -m machine-name -u username -p password |
| Delete | This command deletes a Job Scheduler machine record from the Failover set. |
-d connection-string -m machine-name -u username -p password |
| Failover | This command performs a manual failover. An active Job Scheduler machine is aborted and another machine is specified to take over Job Scheduler functions. |
-d connection-string -m machine-name -u username -p password |
| List | This commands lists the status of all Job Scheduler machines within the failover set. The –t qualifier indicates the refresh interval (in seconds). |
-d connection-string -u username -p password -t interval |
| Modify | This command allows you to modify the preference level of a Job Scheduler machine. The higher the preference-level the more preferred the machine is considered. |
-d connection-string -m machine-name -u username -p password -P priority |
| Policy | This command allows you to change the failover configuration policies. These policies control the checking and timing of failed Job Schedulers. |
-d connection-string -m machine-name -u username -p password -P priority -i interval -l delay -b backup-delay |
|
Start |
This command allows you to start a Job Scheduler service. |
-m machine-name |
|
Stop |
This command allows you to stop a Job Scheduler service. |
-m machine-name |
The above following table lists the commands and qualifiers.
Note: Qualifiers are case-sensitive.
While non-cluster failover is typically free of user intervention, abatavlmgr does allow you to list and otherwise designate a preference or priority order for Job Scheduler machine active startup and failover. The priority is a number from 1 to 10000. The higher the value the more preferred you consider that machine. In a two machine failover set, one Job Scheduler machine will typically be considered primary and the other secondary. When more than 2 machines are present, you can also designate the order for failover recovery. For example, machine A, B and C having a preference-level set to 30, 20 and 10 means that A should become active and then B and C should be considered for standby-to-active failover. Changes to the priority are made through the Modify or Policy command.

The image above is using the AbatAvlMgr List command.
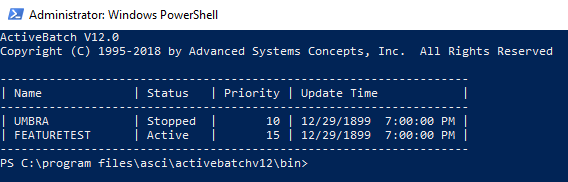
The image above is displaying the results of the List command.
The AbatAvlMgr List command above shows a two (2) machine Job Scheduler failover set. FEATURETEST is the active Job Scheduler machine. Note that its priority of 15 ensures that it will always be selected as the active member in the event a selection needs to be made.
Note: Stopping an active Job Scheduler through the normal Windows service command does not trigger a failover action (unless a lower preferred scheduler machine is in use). This is by design. You can manually request failover action via the Active/Start commands.
Note: As several abatavlmgr commands manipulate the Job Scheduler service you must execute this command from an appropriate administrative level account. In addition, the machine must have host name resolution capability (i.e. you cannot specify an IP address).