Configuring Template Reporting
After you install the ActiveBatch software on a designated system, an ActiveBatch “Management Console” icon will be added to the system’s desktop. In addition, right after the software is installed, the Management Console application will be opened automatically, since this is the next step required in getting your Scheduler environment up and running, and configuring the features you opted to install. The Management Console configuration features are displayed in alphabetical order. To the far right is a Refresh icon which allows you to refresh the properties of the selected component.
Note: The name of the ActiveBatch Management Console application is abatmgmt.exe, located in the bin folder of the ActiveBatch installation directory.
By separating the installation of ActiveBatch features from the configuration of those features and components, it easier and simpler to change configuration parameters without requiring a re-installation or registry modification.
The Management Console is used to configure Template Reporting.
Template Reporting is a facility which allows you to report on all of the various ActiveBatch objects. You can report on those objects and their relationships. A separate help file is available which describes the objects and their relationships. To avoid any adverse impacts on the ActiveBatch transactional database and to also ensure that ActiveBatch itself can be changed and otherwise updated in the future, the Template Reporting facility uses an ETL job which extracts the objects from the transactional database to a new database that is specific to the reporting needs you may have. Separating the databases means that any reports you run won’t have any effect on scheduling and workload automation.
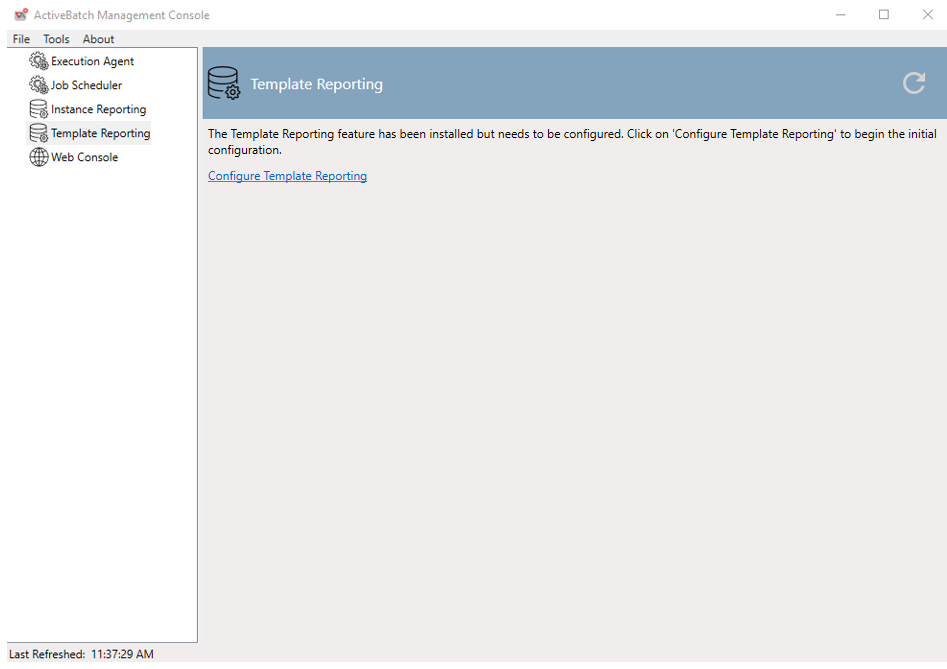
The above dialog symbolizes the beginning of the configuration of Template Reporting. Begin by clicking on the “Configure Template Reporting” link.
Template Reporting Database Family Selection
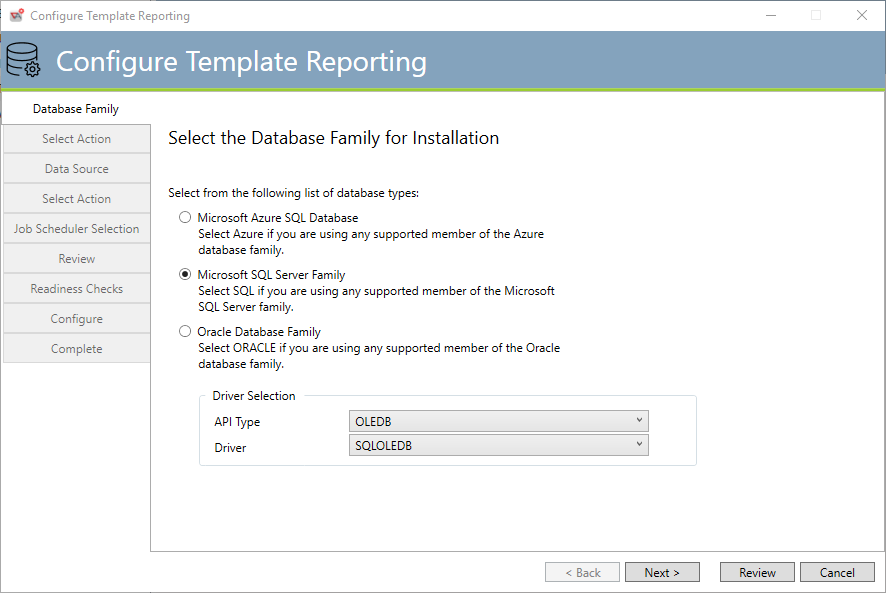
This above dialog asks you to make a selection regarding the database software that you wish to use with Template Reporting.
Note: The selection you make must be the same type that is being used for the Job Scheduler's backend database. For example, if you use MS SQL Server for the backend database, then the Template Reporting database must also be using MS SQL Server.
Microsoft SQL Server represents the various versions of SQL Server supported. See Databases for a list of supported SQL Server database versions. If you don’t have a database, you can download the SQL Express Edition. Azure SQL represents the Microsoft Azure SQL cloud database service. Oracle represents the various versions of Oracle supported. See the above Compatibility KB article link.
If Microsoft Azure SQL or Microsoft SQL are selected, you will have the opportunity to select an OLEDB driver. The driver selected by default should be used unless you are familiar with SQL drivers.
The Back button will move to the previous tab. The Next button will advance to the next sequential tab. The Review button will jump down to the Review tab. For New installations we recommend you click the Next button and look through the most popular component parameters.
See below more details regarding prerequisite requirements for Template Reporting.
Template Reporting Prerequisites - Microsoft SQL Server
SQL Server 2014 or higher
SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) - Optional if you intend to build queries to extract data into this reporting tool. It can be installed on any system that the Job Scheduler can access, and the Execution Agent can access if you are running the SQLServerReport Jobs Library Job Step.
Template Reporting Prerequisites - Oracle
11gR2 for ODAC or higher
ODAC - Required on the Job Scheduler and Execution Agent to run the ETL Job that updates the Template Reporting database. It is also required on the system where the Template Reporting feature is to be configured through the ActiveBatch Management Console.
An ActiveBatch User Account object will need to be created. It will be used to link the Job Scheduler database to the Template Reporting database. The account specified should be the same database account used by the Job Scheduler for backend database access.
Note: While the ActiveBatch Management Console is configuring the reporting feature, the Job Scheduler database user and the newly created Reporting database user will need to be granted the CREATE PUBLIC DATABASE LINK, otherwise, the configuration may fail with missing permissions. As an alternative, a DBA may create the Reporting database user with the required permissions and then the ActiveBatch Administrator would select the “Update an Existing Database” option during configuration.
If Microsoft SQL Server or Azure SQL was selected, continue reading this section.
If Oracle was selected, continue to section Template Reporting Database Operation (Oracle).
Template Reporting Database Operation (SQL)
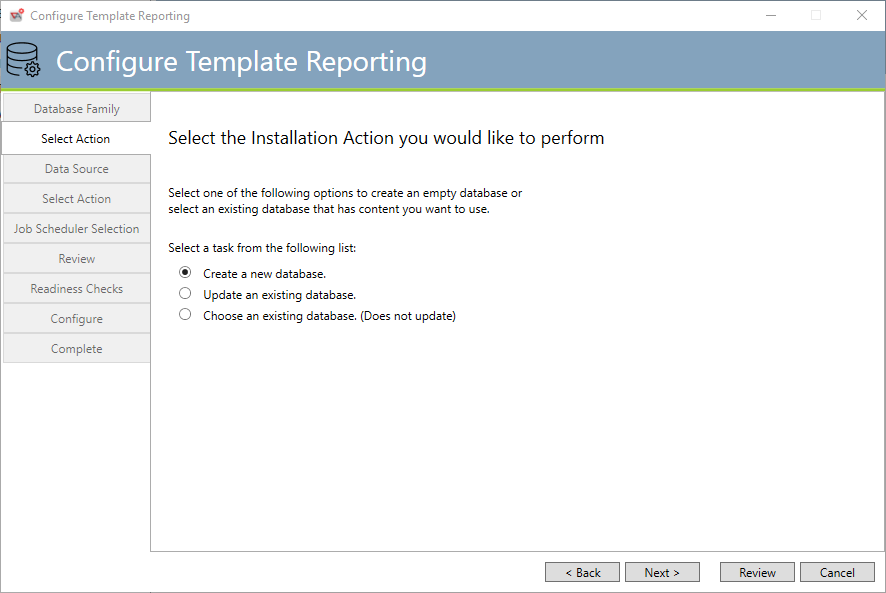
The above dialog asks you to make a selection as to the state of the Template Reporting database.
Create a new database (default) means that you have not created an empty database (or tablespace) for ActiveBatch to use for Template Reporting. New ActiveBatch users would typically make this selection.
Update an existing database means that you have an existing Template Reporting database that you would like to use and update or if no Template Reporting tables exist we will add our tables to this database.
Choose an existing database (Does not update) means that you would simply like this configuration to use an existing database.
If Create a new database was selected, then continue to the next page. If the other choices were selected, please continue to section Template Reporting Update an Existing Database (SQL).
Template Reporting Database
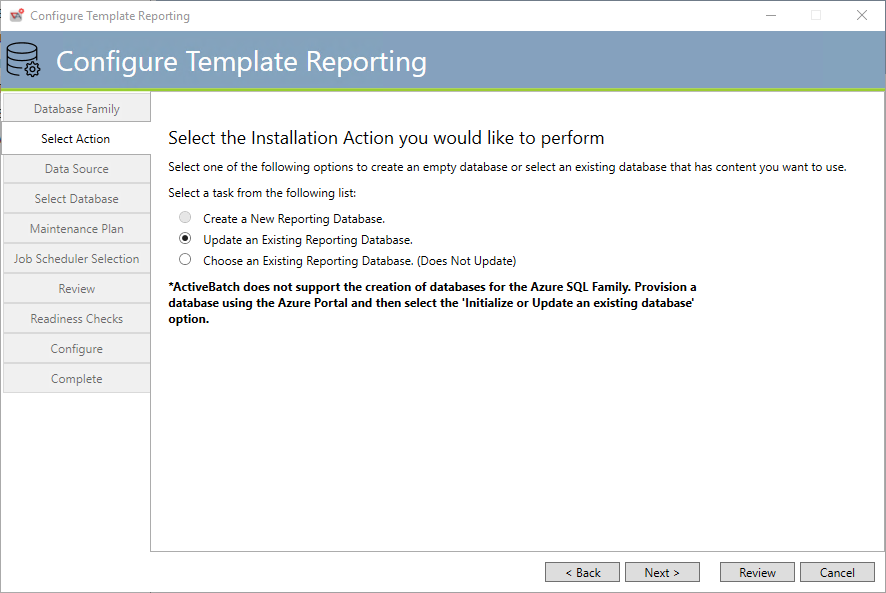
ActiveBatch does not support the direct creation of an Azure SQL database for ActiveBatch purposes. This is due to costs incurred using Microsoft and their services. We believe that you should make the size and selection of the database, directly. So you must use the Microsoft Azure portal to create an empty database and then execute the installation. We do highly recommend that you select an S4 or larger database sizing option.
The Back button will move to the previous tab. The Next button will advance to the next sequential tab. The Review button will jump down to the Review tab. For New installations we recommend you click the Next button and look through the most popular component parameters.
Template Reporting Database Data Source (SQL)
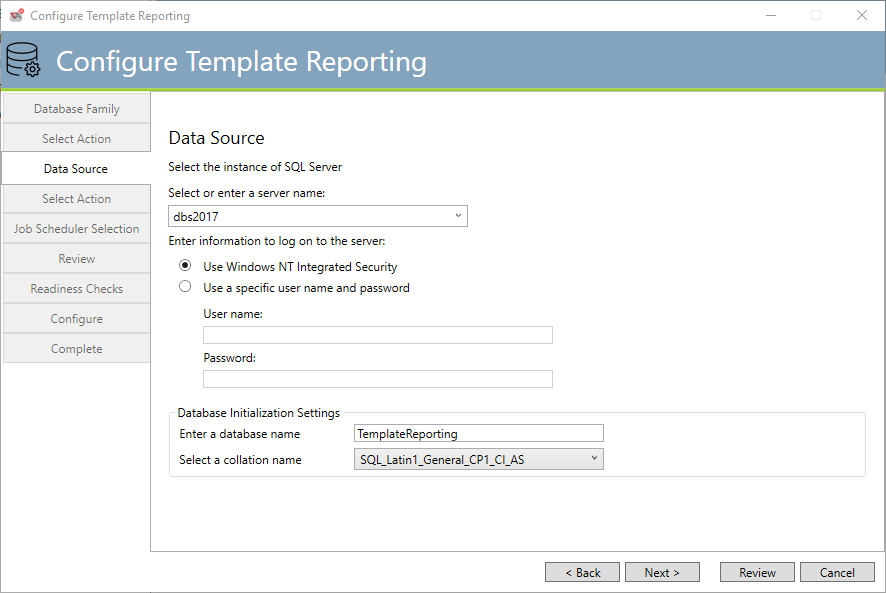
The above dialog asks you to select a machine that is running the SQL Server instance you need. The lower half of the dialog addresses authentication.
Using the dropdown, select a machine that is running the SQL Server software that you want ActiveBatch to use. If your desired machine is not shown you may type it in (just the machine name and, if applicable, instance name) and the installation will attempt to connect to it. The example above is referencing the SQL Server product on machine dbs2017. If the product was SQL Server Express the instance would be named “sqlexpress” (the syntax is “machine-name\instance-name”). In that case, dbs2017\SQLEXPRESS would unambiguously reference that instance on the dbs2017 system.
SQL Server supports two types of authentication: Windows Integrated Authentication and Database.
Windows Integrated Authentication refers to the normal Windows security system. This means that the user account you specify for the Job Scheduler service will be used to access the database. That account must be given full access. Database refers to the database’s own authentication.
Note: The “Username” specified is not a Windows username but a database user.
Under the Database Initialization Setting
For the first field, you will need to enter the name of the database you want to create.
For the second field, you will need to select a collation name. You can specify any collation name as long as it is “case insensitive” (assuming the language supports the concept of case). Look for _CI_ in the collation name for a case insensitive language collation name.
The Back button will move to the previous tab. The Next button will advance to the next sequential tab. The Review button will jump down to the Review tab. For New installations we recommend you click the Next button and look through the most popular component parameters.
Template Reporting Update an Existing Database (SQL)
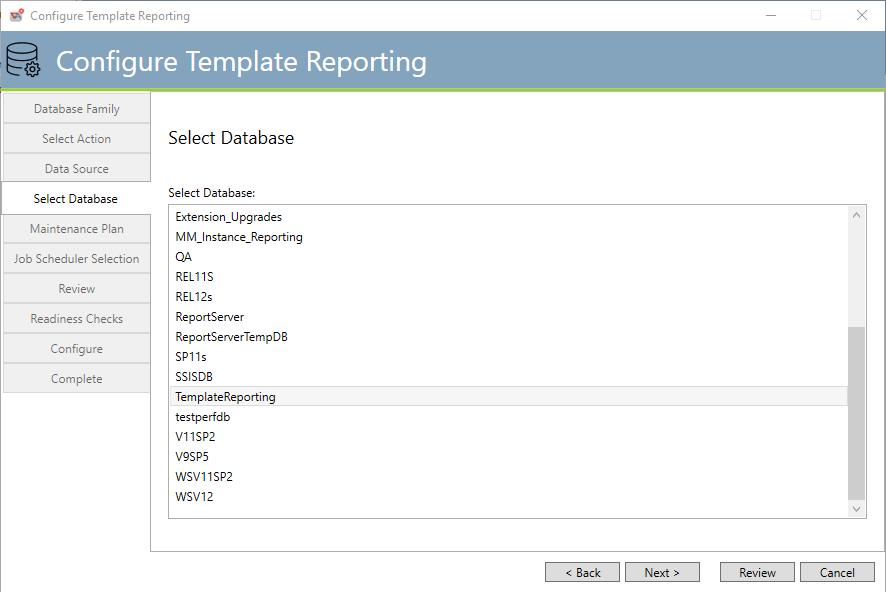
Updating an existing database consists of requesting the Data Source. Once you’ve entered the Data Source, the above dialog appears.
After a slight pause, a large list box will appear with all the databases your selected SQL Server machine offers. Select the database you want to use for V12 Template Reporting. If ActiveBatch V9 through V11 tables are detected those tables will be upgraded to V12. If ActiveBatch tables are not detected, we will create those tables and all necessary ActiveBatch database objects within the database.
The Back button will move to the previous tab. The Next button will advance to the next sequential tab. The Review button will jump down to the Review tab. For New installations we recommend you click the Next button and look through the most popular component parameters.
Template Reporting Database Operation (Oracle)

The above dialog asks you to make a selection as to the state of the Template Reporting database.
Create a new database: (default) This means that you have not created an empty database (or tablespace) for ActiveBatch to use for Template Reporting. New ActiveBatch users would typically make this selection.
Update an existing database: This means that you have an existing Template Reporting database that you would like to use and update or if no Template Reporting tables exist we will add our tables to this database.
Choose an existing database (Does not update): This means that you would simply like this configuration to use an existing database.
If “Create a new database” was selected then continue to the next page. If the other choices were selected, please continue to section Template Reporting Data Source – Existing (Oracle).
Template Reporting Schema Settings – New (Oracle)
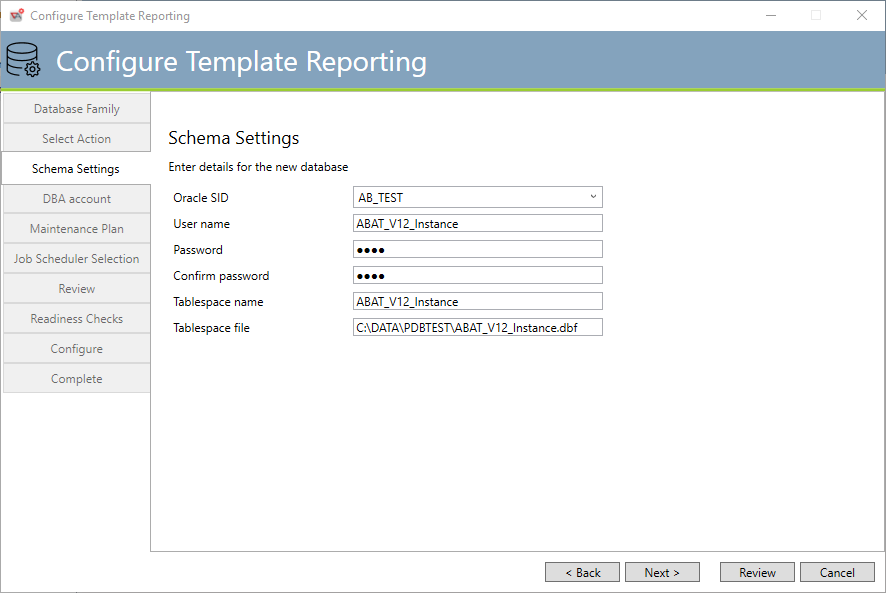
The above dialog requests various information needed to initialize a tablespace for ActiveBatch Template Reporting purposes.
Oracle SID: This refers to “Service ID” or the database server/instance that hosts the database.
User/Schema Name This refers to the database user that is used to form the schema name that ActiveBatch will use for its tables.
Tablespace name: This is the name of the tablespace that the configuration process will add the ActiveBatch database objects to. The default specification is “abat”.
Tablespace File refers to the physical location of the tablespace (for example, C:\OracleXE\OraData\XE\Abat.dbf).
Note: The Schema User will be granted the following Oracle privileges: Create Session, Alter Session, Create Table, Create View, Create Procedure, Create Sequence, Create Trigger, Create Type, Connect, Grant on SYS.DBMS_SESSION and Grant Any Context for ABAT_schema-user.ABAT_SETCONTEXT.
If you receive an Oracle “Insufficient Privileges” error it is almost always due to one or more missing privileges from the above list.
The Back button will move to the previous tab. The Next button will advance to the next sequential tab. The Review button will jump down to the Review tab. For New installations we recommend you click the Next button and look through the most popular component parameters.
Template Reporting DBA Account (Oracle)
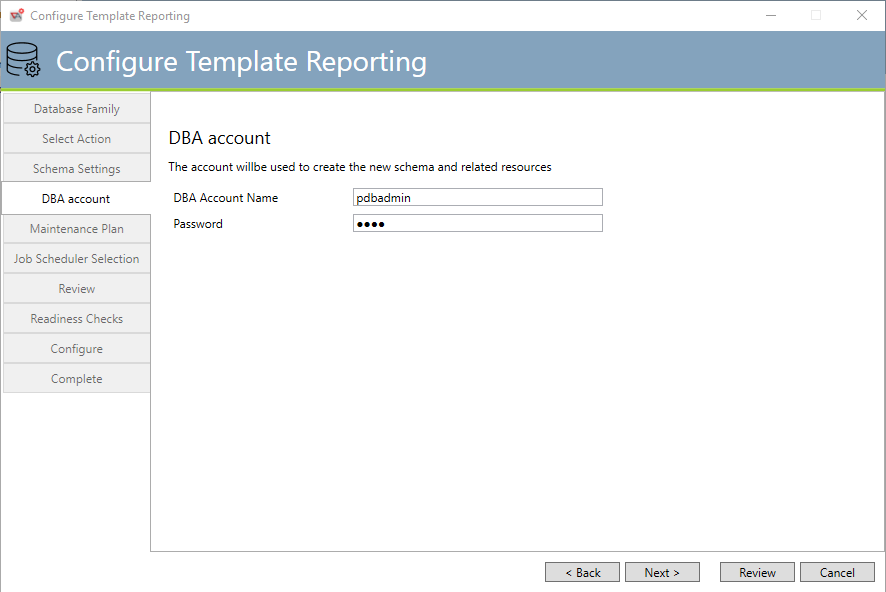
DBA level access is required to create the Template Reporting schema. The above dialog requests a system level user and password with which the installation process will be able to add the schema to the previously named tablespace.
The Back button will move to the previous tab. The Next button will advance to the next sequential tab. The Review button will jump down to the Review tab. For New installations we recommend you click the Next button and look through the most popular component parameters.
Template Reporting Data Source – Existing (Oracle)
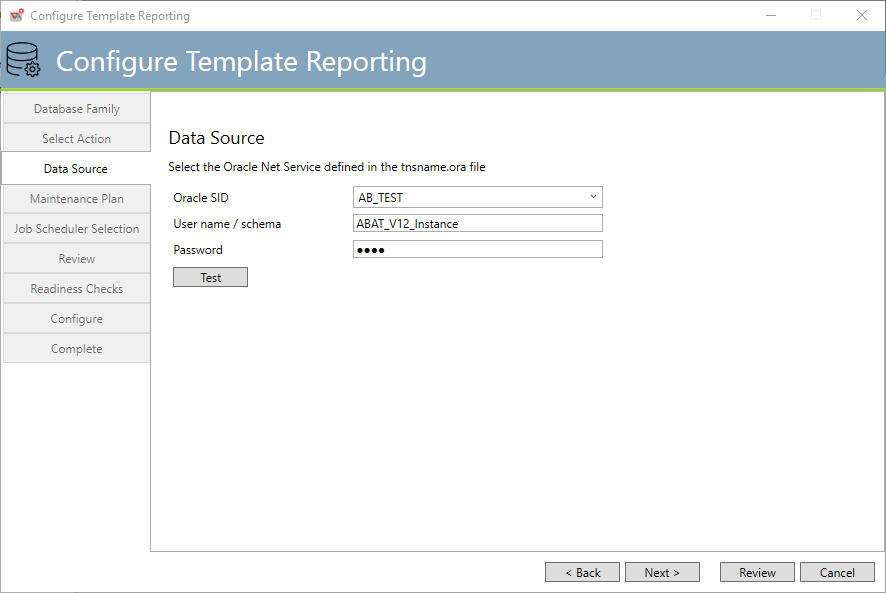
Oracle SID: This is the Oracle SID that represents the Oracle database instance/server that hosts the tablespace.
Username/Schema/Password: This is the security information that represents the schema user.
Click the Test button to verify that the account and password specified are proper.
The Back button will move to the previous tab. The Next button will advance to the next sequential tab. The Review button will jump down to the Review tab. For New installations we recommend you click the Next button and look through the most popular component parameters.
Template Reporting Maintenance Plan
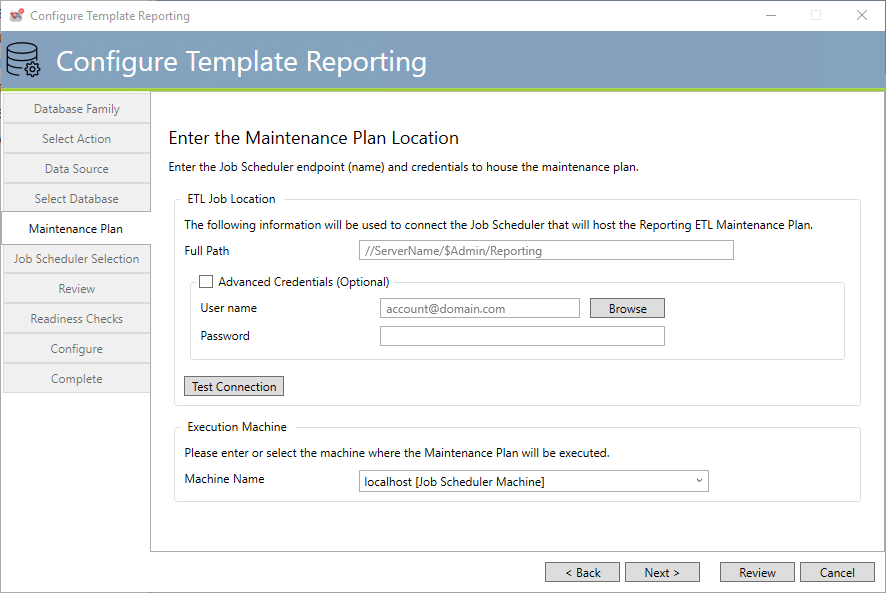
This tab configures the ActiveBatch ETL job that will be used to extract ActiveBatch objects from the operational system to the Template Reporting database.
Full Path: This property consists of a Job Scheduler hostname (which may optionally be fully qualified) and the remaining portion of the path to the object ($Admin/Reporting) which should not be changed. For example, //DevJSS/$Admin/Reporting indicates that this ETL job is for the Job Scheduler residing on the DevJSS system.
By default, the configuration program will use your logged in Windows credentials to establish the connection to the specified Job Scheduler. If your credentials are insufficient, please enable the Advanced Credentials area and specify a different username and password that should be used to perform the ETL job creation.
We recommend that you click the Test Connection button to verify that the proper connection to the specified Job Scheduler can be made.
The Back button will move to the previous tab. The Next button will advance to the next sequential tab. The Review button will jump down to the Review tab. For New installations we recommend you click the Next button and look through the most popular component parameters.
Template Reporting Job Scheduler Selection
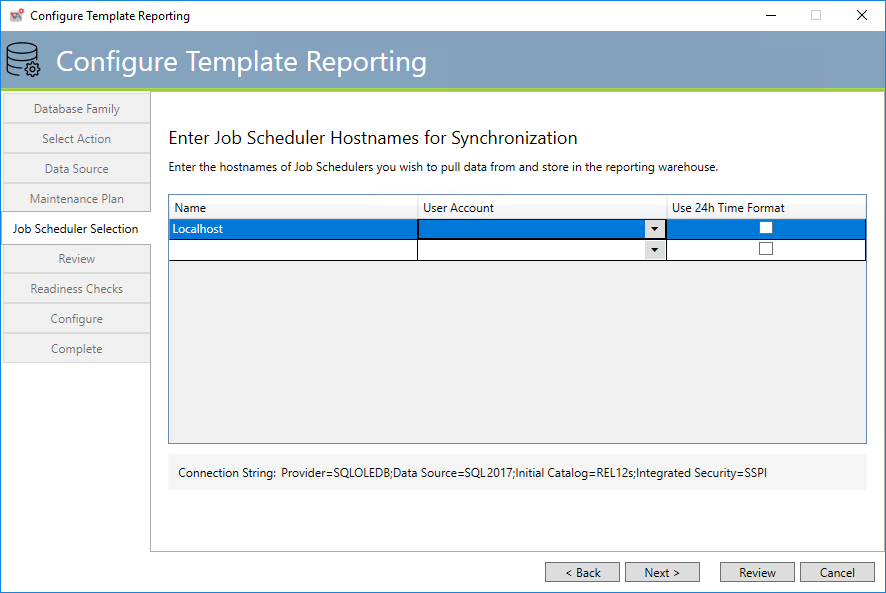
This tab is used by the ETL Maintenance Program (which was defined on the previous tab) to define which Job Scheduler database(s) are to be the subject of the “Extract” of the ETL job.
Name: Hostname of the desired Job Scheduler. The Job Scheduler will be contacted and its database connection string will be used to connect and extract the relevant ActiveBatch objects.
User Account: User Account object that will be used to access the Job Scheduler database.
Use 24h Time Format: If enabled, 24-hour format will be used for time specifications.
The Back button will move to the previous tab. The Next button will advance to the next sequential tab. The Review button will jump down to the Review tab. For New installations we recommend you click the Next button and look through the most popular component parameters.
Template Reporting Review
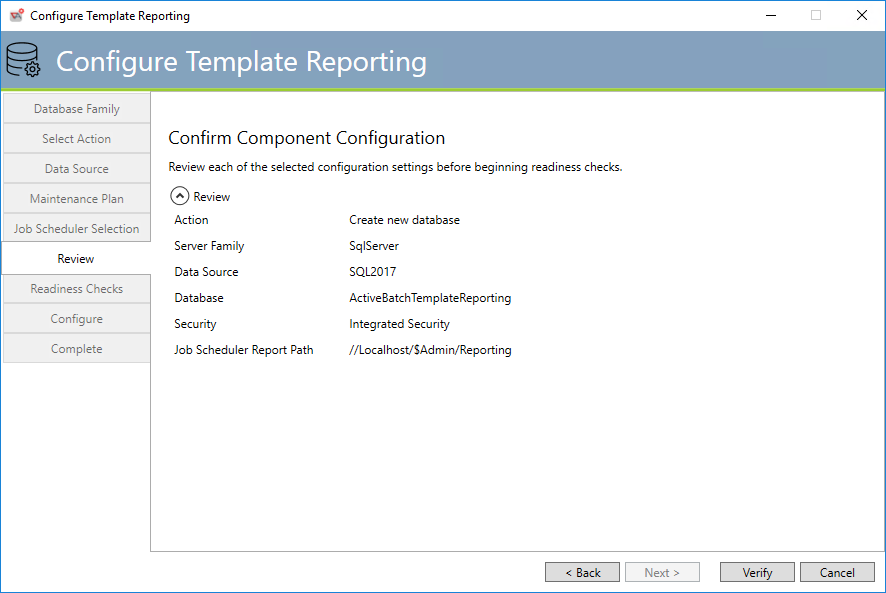
This tab allows you to review the Template Reporting database answers you’ve provided.
You may click the Back button to go backward to a tab and change an answer or click the Verify button to continue and perform Readiness checks.
Template Reporting Readiness Checks
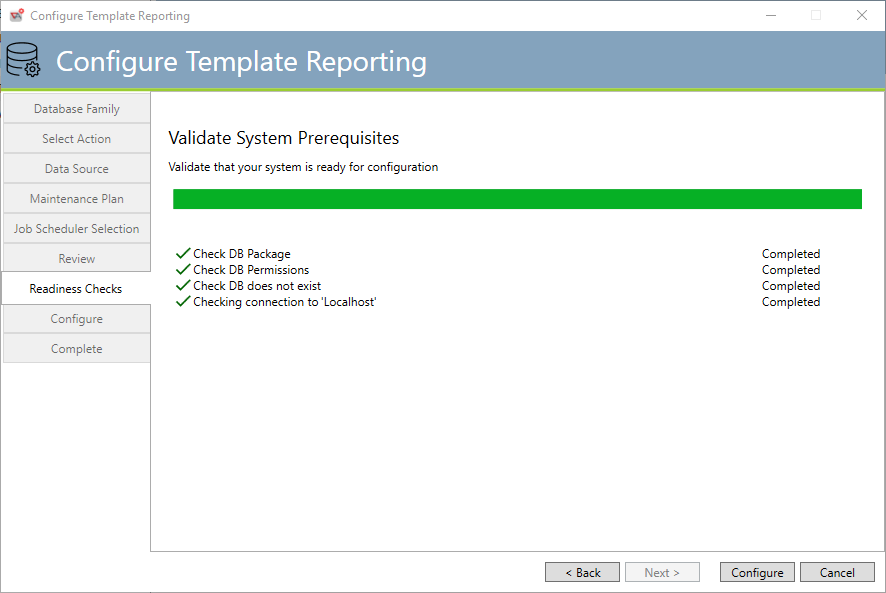
This tab performs readiness checks on the various properties that were specified on the earlier tabs.
Template Reporting Configuration
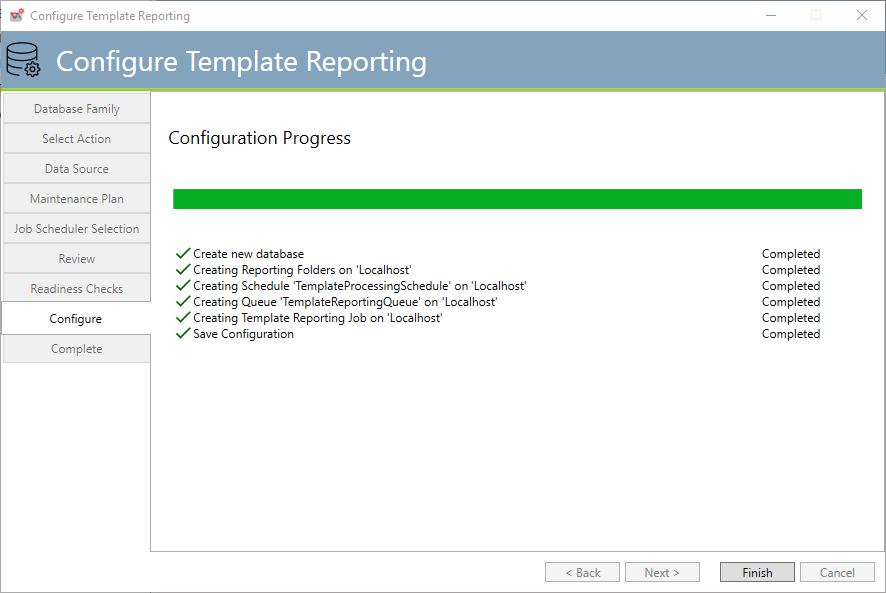
This tab performs the actual configuration as it relates to Template Reporting. Any errors are noted above.
Template Reporting Configuration Complete
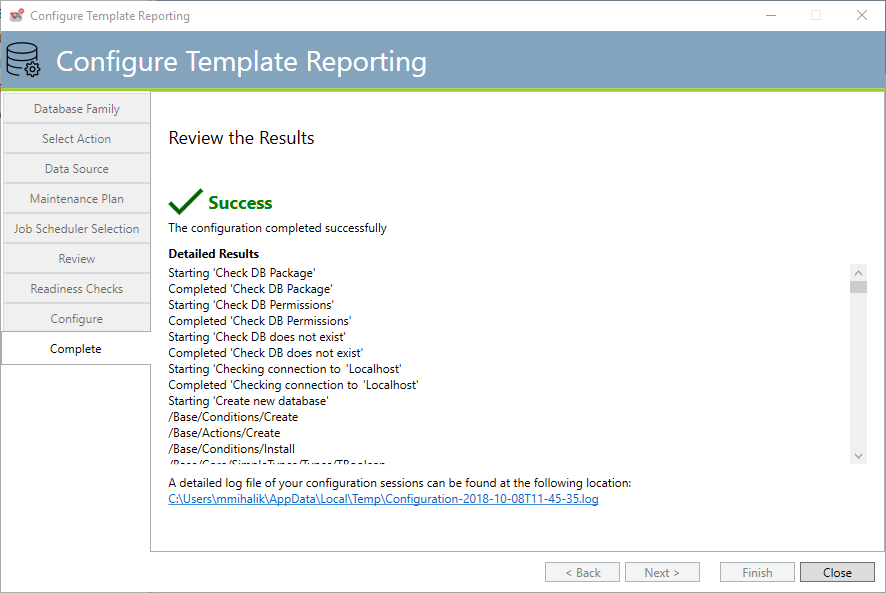
This tab provides a log of all the operations performed to configure Template Reporting.