 Snowflake
Snowflake
Snowflake provides cloud-based data storage providing analysis and access to multiple data sets simultaneously with very little latency. Snowflake is compatible with Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
The Snowflake extension allows users to create and manage automated Snowflake processes. See Snowflake Permissions for details on the required permissions.
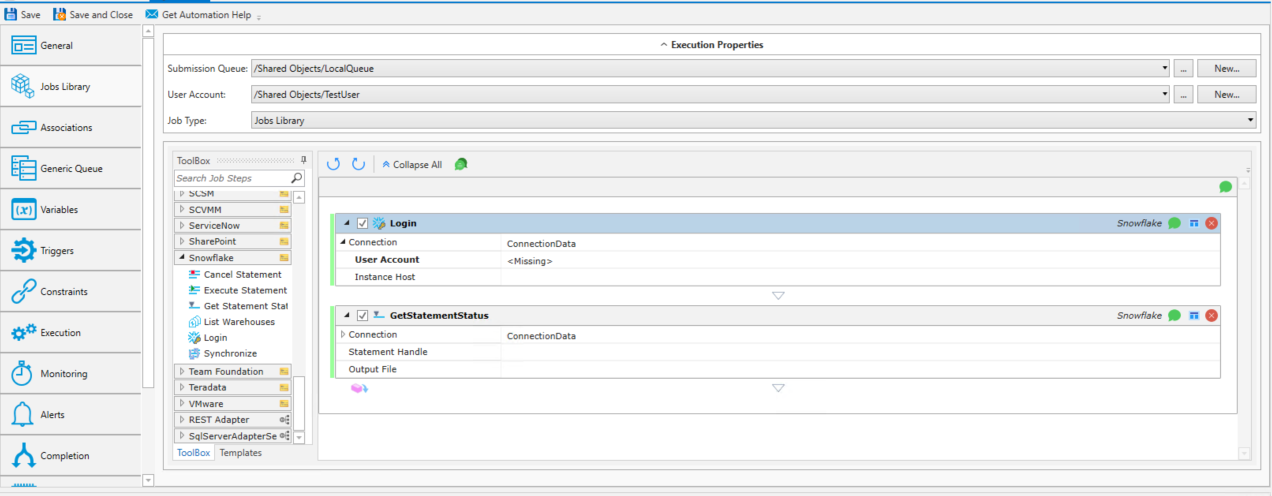
Login

Sets authenticated session for subsequent job steps.
Job Step Properties
Connection: Connection is optional for all Job Steps except Login. Select Connection Data from the drop-down menu and enter a User Account and
Region.
User Account: Select Connection Data from the drop-down menu and enter a User Account. Snowflake requires a RestV2 OAuth user with a grant type = authorization code.
(Refer to your Snowflake documentation for information on how to Configure Snowflake OAuth for custom clients.)
Instance Host: (Optional) If blank, the Auth Token URL of the User Account will be used.
GetStatementStatus

Connection: If not specified by the Login Job Step, this field is required. Select Connection Data from the drop-down menu and enter a User Account and
Region.
Statement Handle: The statement handle to use when getting the current status.
Output File: The output file to use for the final query results.
List Warehouses

Connection: Connection data for the Snowflake instance.
Pattern: Used to filter the command output by resource name.
Synchronize

Connection: Connection data for the Snowflake instance.
Statement Handle: The statement handle to use when getting the current status.
Output File: The output file to use for the final query results.
Execute Statement
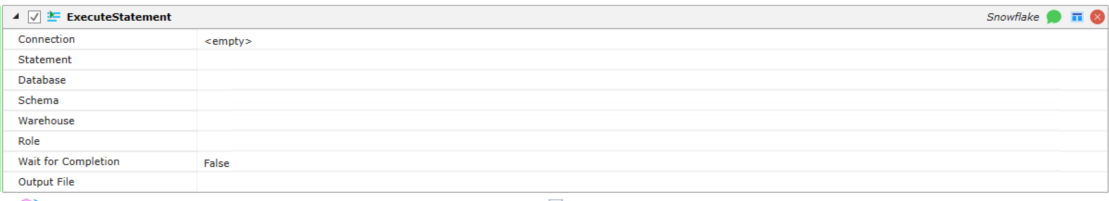
Connection: Connection data for the Snowflake instance.
Statement: SQL statement to execute. A call can be made to a stored procedure by using CALL stored_procedure_name().
Database: Database where the statement will be executed.
Schema: Schema where the statement will be executed.
Warehouse: The warehouse to use when executing the statement.
Role: The role to use when executing the statement.
Wait for Completion: Whether or not to wait for the statement to finish executing. True/False.
Output File: Final query results output file.
Cancel Statement

Connection: Connection data for the Snowflake instance.
Statement Handle: The statement handle to use when getting the current status.
Snowflake Permissions
These are the minimum permissions required for all job steps to work in Snowflake.
Note: Environments vary! You may need additional permissions or roles.
MONITOR WAREHOUSE:This is typically added to a Role in order to view warehouses. This must be added to any warehouse the account needs access to view.
USAGE on the Warehouse
-
The role executing the statement must have the USAGE privilege on the virtual warehouse where the statement will be run.
Permissions on Database Objects
-
The role must have the necessary privileges (e.g., SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE TABLE, USAGE on schema/database) on the specific database objects (tables, views, schemas, databases) that the statements interact with.
USAGE on Stored Procedures and Functions
-
If the statement calls a stored procedure or user-defined function, the role needs USAGE privilege on that stored procedure or function.
Note: Any user with execute privilege can cancel their own running SQL operation without needing additional privileges.