Queue Counters
Queue Counters View provides a list of all queues present within the connected Job Scheduler and their respective counters.
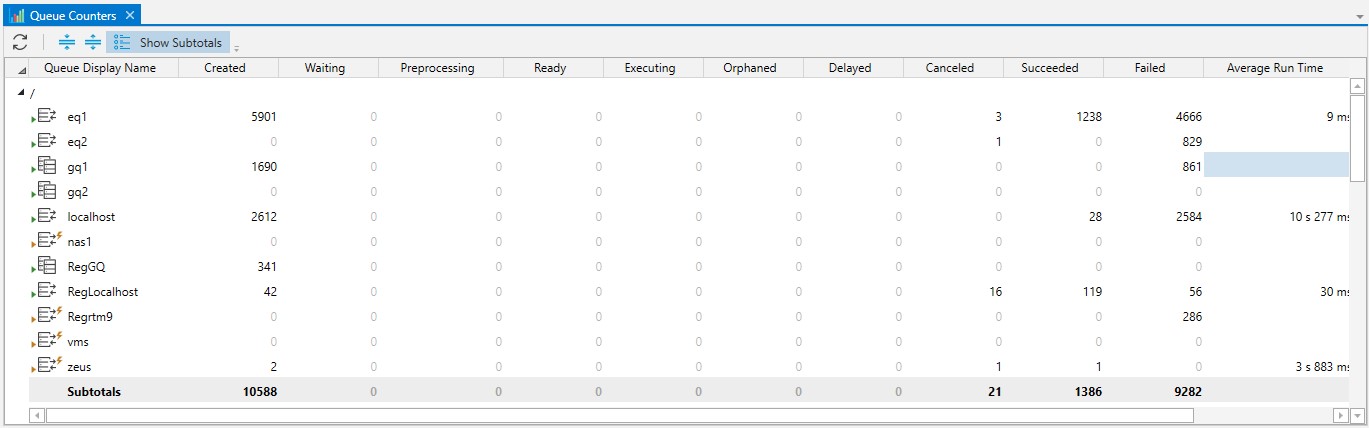
The view is list oriented with each queue and its associated counters on a separate row. The queues are shown in color to denote their current state and this view consolidates all queues (regardless of root or plan location) within a single view.
Note: Note: Queue Counters is not a real-time dynamic view. You must click the Refresh button to see any changes to the counters.
Note: You will not be able to select Queue Counters from a newly added, but checked-out Execution/Generic Queue. The Queue object must be checked-in for this view to be available.
The Queue Counters view provides you with insight as to where your Generic and Execution Queues are specified. For each queue row, a set of counters are provided. Most of the counters are self-explanatory. Counters such as Executing or Waiting are operational in nature and reflect the current number of jobs/plans in each state. Some counters are historical and indicate the total number of objects that were present in that state. For example, Succeeded or Failed show the number of jobs which were successful or failed (and thus are only incremented). Finally, a set of counters indicate the average run-time or CPU time that a job on that queue encountered. At the very end of the view is a “Totals” row. By default, sub-totals are not displayed for each level, however, if you click the “Subtotals” button, then subtotals will appear at the bottom of each level.
Icons along the Queue Counter View’s toolbar are: Refresh, Collapse All, Expand All and Show Subtotals.
A set of counters are present for Managed Queues, when used. Managed Queues require additional licensing for the VM or Cloud environment you are using this feature with. The Managed Queue counters are Avg. Start Time, Active Machines and Inactive Machines. The “Avg. Start Time” represents the average instantiation time it took to provision and bring up a machine for usability purposes. Active Machines are those systems which are up and running and being used. Inactive Machines are those machines which have been started but are not being used due to inactivity.